
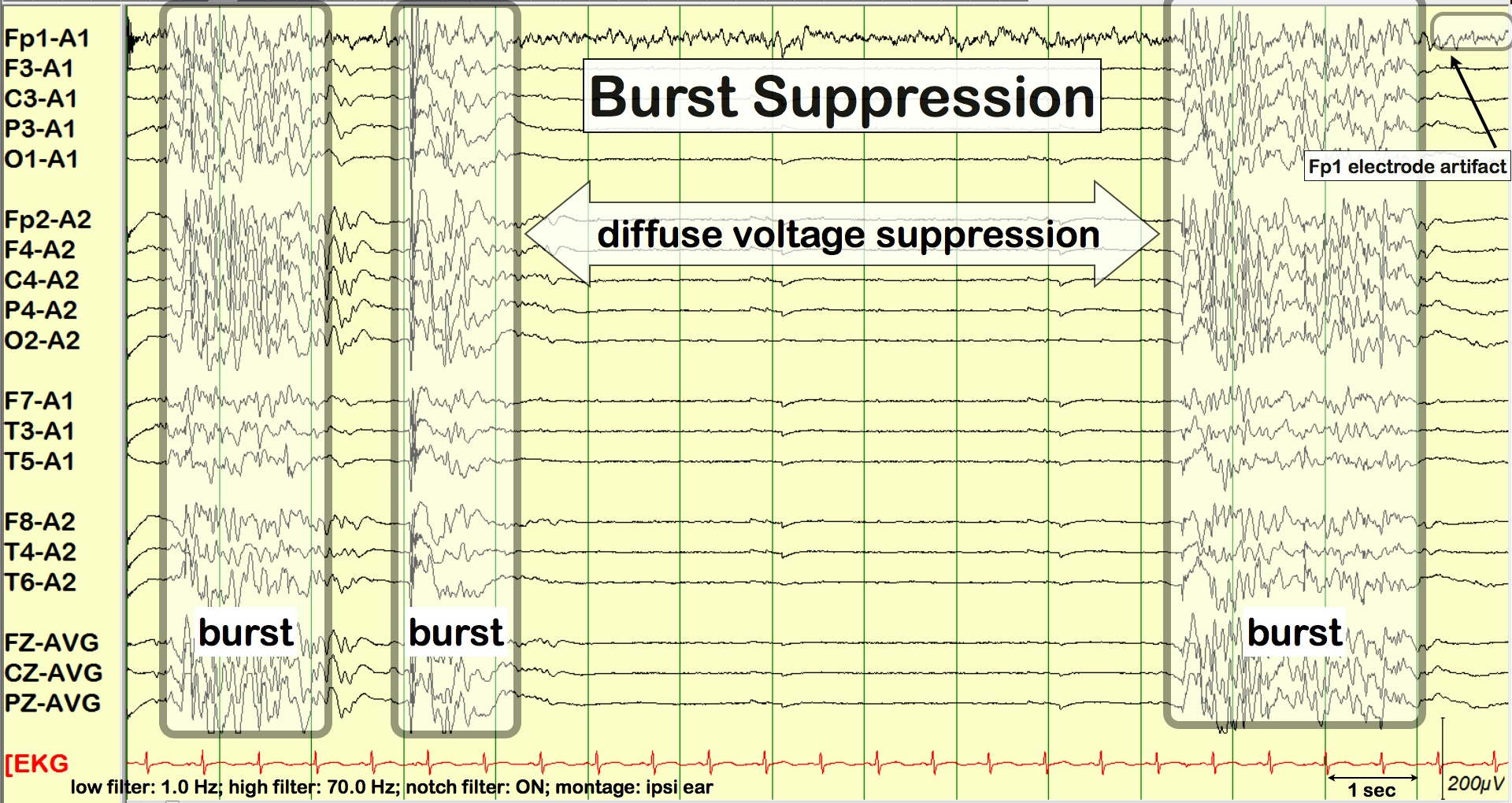
Maximum burst amplitudeĪB - Background: Refractory status epilepticus (RSE) is often treated with continuous intravenous medications with the goal of EEG burst suppression. The interburst intervals, burst suppression ratios, and length of bursts did not differentiate successful and unsuccessful lifting attempts the amount of epileptiform activity in bursts correlated with success or failure to wean IVAT (p = 0.008). Results: We included 17 successful and 20 unsuccessful lifting attempts in 19 patients (5 used as a holdout validation set). We compared these characteristics in successful versus unsuccessful IVAT lifting attempts. We measured the length of bursts and interburst intervals for each patient, calculated EEG burst suppression ratios, and graded bursts for the amount of epileptiform activity. Methods: We screened the clinical continuous EEG database for adult patients treated with IVAT for RSE (excluding patients with anoxic injury). We examined EEG characteristics in patients treated with IV anesthetic therapy (IVAT) for RSE to determine which EEG characteristics were associated with successful lifting of IVAT (i.e., without recurrence of status epilepticus). Standard advice is to titrate medications to at least 10-s interburst intervals however, this has not been shown to improve outcome. N2 - Background: Refractory status epilepticus (RSE) is often treated with continuous intravenous medications with the goal of EEG burst suppression. T1 - EEG Characteristics of Successful Burst Suppression for Refractory Status Epilepticus Maximum burst amplitudeĪbstract = "Background: Refractory status epilepticus (RSE) is often treated with continuous intravenous medications with the goal of EEG burst suppression. Background: Refractory status epilepticus (RSE) is often treated with continuous intravenous medications with the goal of EEG burst suppression.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
